How Smoking Impacts Every Organ in the Human Body
How Smoking Impacts Every Organ in the Human Body

Smoking has a devastating impact on nearly every organ in the human body, leading to a wide range of health problems:
Respiratory System: Smoking damages the lungs, causing diseases like COPD, emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and lung cancer. It also weakens the immune defenses of the airways, increasing the risk of infections.
Cardiovascular System: Smoking harms blood vessels, raising the risk of heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure. It causes a buildup of plaque in arteries and increases blood clotting.
Nervous System: Nicotine addiction affects the brain’s reward system and increases the risk of stroke. Smoking also harms cognitive function, potentially leading to conditions like dementia.
Digestive System: Smoking contributes to cancers of the mouth, throat, esophagus, pancreas, and stomach. It also increases the risk of gastric ulcers and GERD.
Immune System: Smoking weakens the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and increasing the risk of autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis.
Integumentary System (Skin, Hair, Nails): Smoking accelerates skin aging, causing wrinkles and dullness, and slows wound healing.
Reproductive System: Smoking reduces fertility in both men and women, and increases the risk of complications during pregnancy, such as miscarriage, low birth weight, and SIDS.
Urinary System: Smoking raises the risk of bladder and kidney cancer and can lead to kidney damage over time.
Musculoskeletal System: Smoking weakens bones, leading to osteoporosis and a higher risk of fractures. It also delays muscle recovery and healing.
Endocrine System: Smoking disrupts hormonal balance, raising the risk of type 2 diabetes, metabolic disorders, and hormonal imbalances.
Read Article into details
🔬 1. Respiratory System (Lungs, Airways)
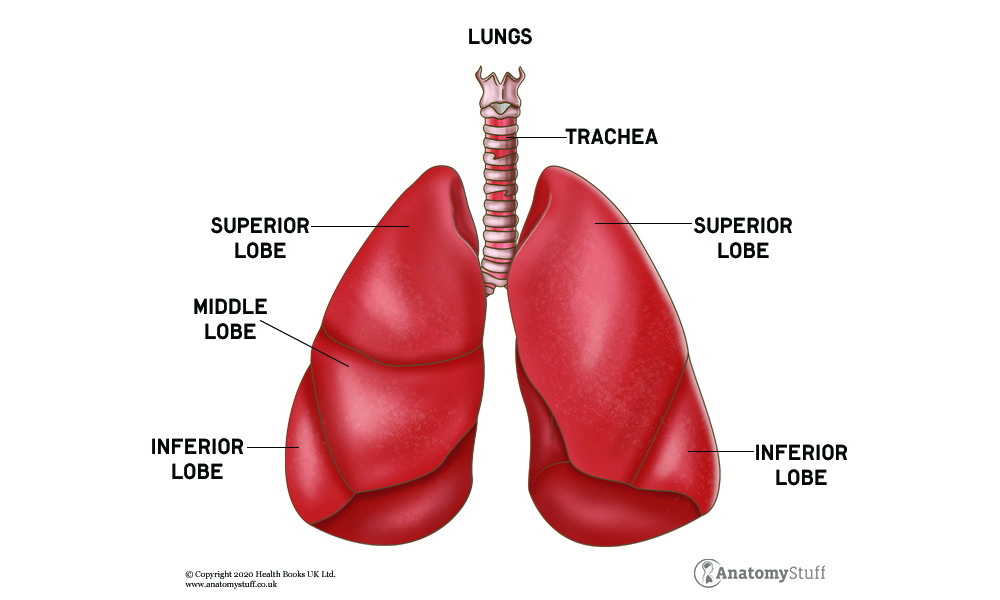
Primary Effects:
- Chronic inflammation: Tobacco smoke irritates the lining of the airways and alveoli (tiny air sacs in the lungs), triggering inflammation.
- Cilia damage: Cilia (tiny hair-like structures that sweep out mucus and debris) are paralyzed or destroyed, reducing the lungs’ ability to clear infections.
- Loss of elasticity: Smoking destroys alveolar walls, leading to emphysema (a form of COPD) — lungs lose their ability to expand and contract effectively.
Diseases:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Lung cancer (smoke contains >70 carcinogens, including benzo[a]pyrene)
- Asthma exacerbation
- Respiratory infections (bronchitis, pneumonia)
❤️ 2. Cardiovascular System (Heart & Blood Vessels)

Primary Effects:
- Endothelial damage: Chemicals in smoke damage the lining of arteries (endothelium), promoting atherosclerosis (plaque buildup).
- Increased clotting: Smoking increases fibrinogen levels and platelet aggregation, making blood thicker and more likely to clot.
- Reduced oxygen: Carbon monoxide in smoke binds to hemoglobin more strongly than oxygen, depriving tissues of oxygen.
Diseases:
- Heart attacks (myocardial infarction)
- Stroke
- Peripheral artery disease
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
🧠 3. Nervous System (Brain and Nerves)

Primary Effects:
- Nicotine: Stimulates the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine, creating addiction and temporary pleasure, followed by withdrawal and craving.
- Vasoconstriction: Nicotine constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the brain.
Diseases:
- Increased risk of stroke
- Cognitive decline (potential link to dementia)
- Addiction and withdrawal symptoms (irritability, anxiety, depression)
🍽️ 4. Digestive System
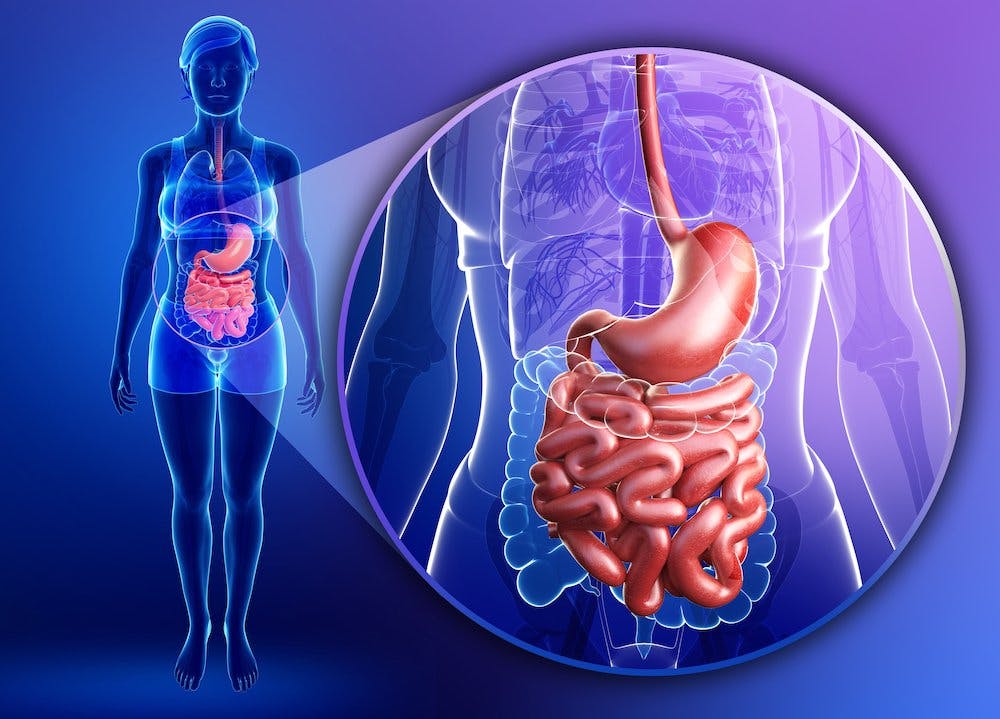
Primary Effects:
- Gastrointestinal irritation: Smoking increases stomach acid and decreases protective mucus, harming the stomach lining.
- Carcinogens: Ingested or absorbed carcinogens are transported to digestive organs through the bloodstream.
Diseases:
- Cancers: Mouth, throat, esophagus, pancreas, liver, colon, and stomach
- Gastric ulcers
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
🛡️ 5. Immune System

Primary Effects:
- Immune suppression: Smoking reduces white blood cell activity and antibody response.
- Chronic inflammation: Persistent exposure leads to an overactive immune system and higher baseline inflammation.
Diseases:
- Increased risk of infections (flu, pneumonia, tuberculosis)
- Autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Slower recovery from illness and surgery
🧬 6. Integumentary System (Skin, Hair, Nails)
Primary Effects:
- Vasoconstriction: Reduces blood flow to the skin, leading to poor oxygen and nutrient supply.
- Collagen degradation: Tobacco smoke breaks down collagen and elastin — proteins responsible for skin elasticity and firmness.
Consequences:
- Premature aging (wrinkles, sagging)
- Delayed wound healing
- Higher risk of skin conditions like psoriasis
👶 7. Reproductive System
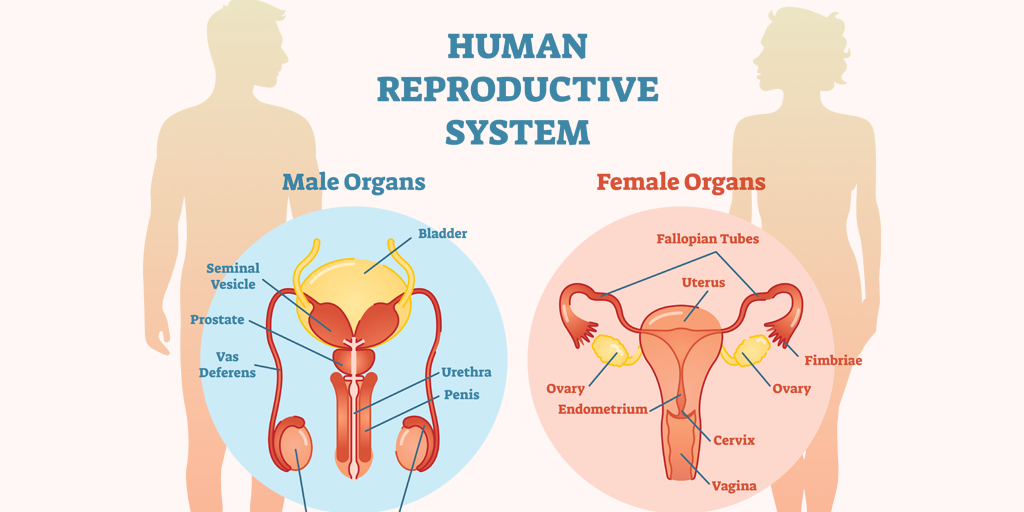
In Men:
- Reduced sperm count and motility
- Erectile dysfunction due to impaired blood flow and vascular damage
In Women:
- Decreased fertility
- Early menopause
- Menstrual irregularities
Pregnancy Risks:
- Miscarriage
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Low birth weight
- Stillbirth
- Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
💧 8. Urinary System (Kidneys, Bladder)
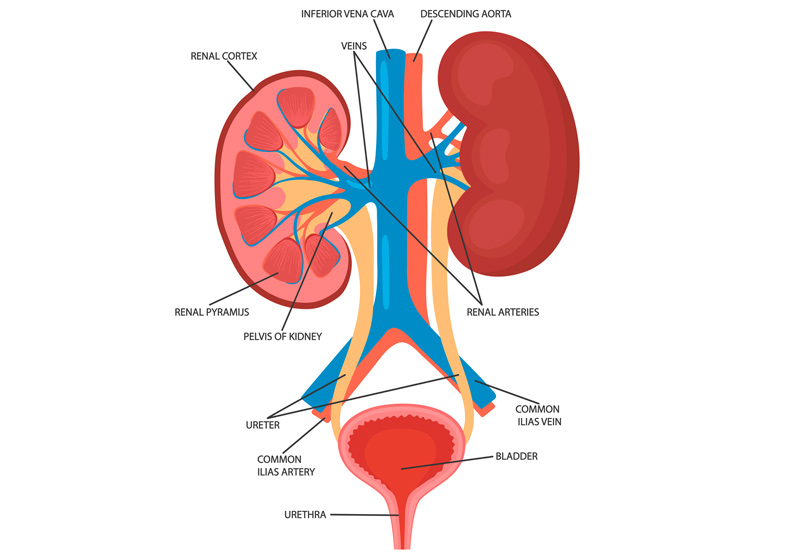
Primary Effects:
- Carcinogen filtration: Kidneys filter blood and excrete chemicals from tobacco smoke into urine, which sits in the bladder.
Diseases:
- Bladder cancer (linked directly to carcinogens in smoke)
- Kidney cancer
- Reduced kidney function over time
🦴 9. Musculoskeletal System
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1053029940-9bffdb28ff5147048b02c65a91c48436.jpg)
Primary Effects:
- Bone weakening: Smoking lowers estrogen levels and calcium absorption, weakening bones.
- Muscle damage: Reduced oxygen and blood flow impair muscle repair and function.
Diseases/Effects:
- Osteoporosis (especially in women)
- Increased risk of fractures
- Slower healing of broken bones and wounds
🔄 10. Endocrine System (Hormones)
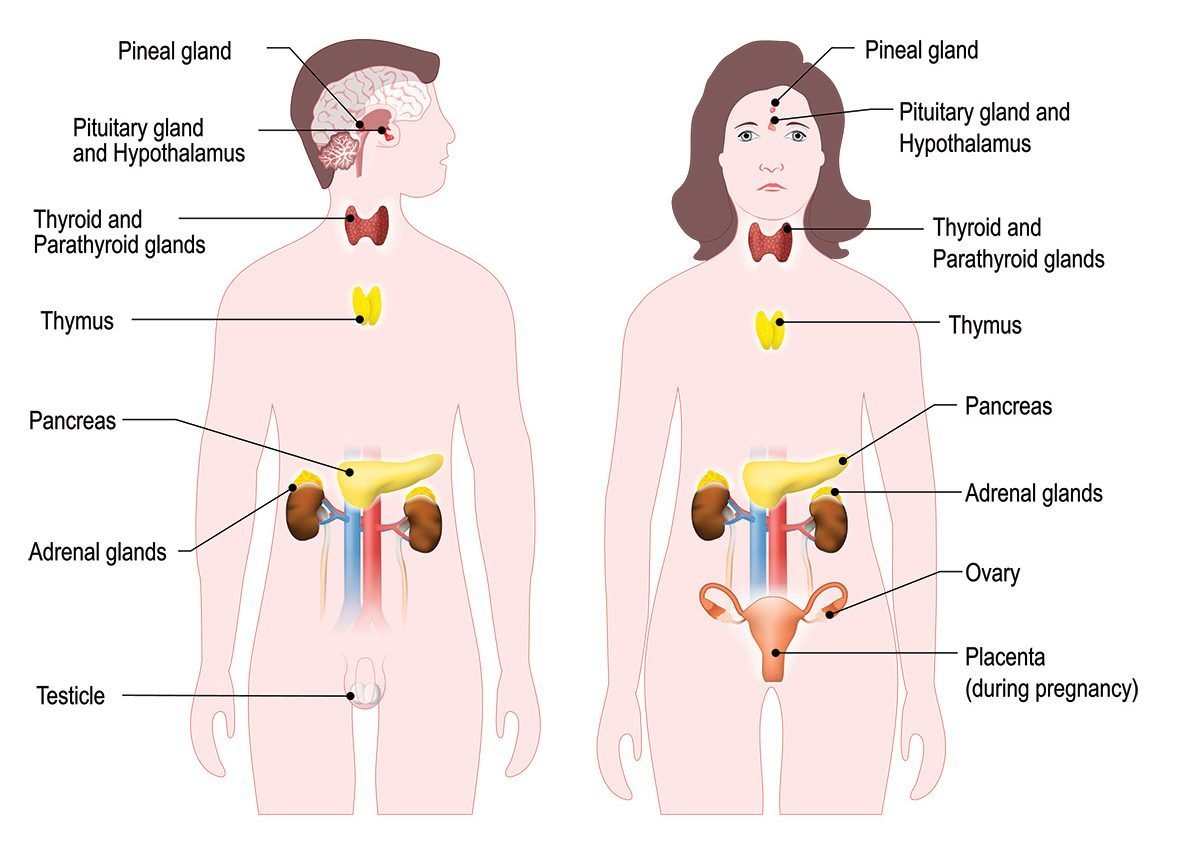
Primary Effects:
- Hormonal disruption: Smoking alters levels of insulin, estrogen, testosterone, cortisol, and thyroid hormones.
- Insulin resistance: Nicotine interferes with insulin signaling, raising blood sugar levels.
Diseases:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Hormonal imbalances
- Complications in metabolic syndrome
Summary:
Smoking harms nearly every organ, mostly due to:
- Over 7,000 chemicals, hundreds of which are toxic
- At least 70 known carcinogens
- System-wide inflammation, oxidative stress, and cellular damage
Caution– For approval to receive payment DON’T skip Task
TASK- Click below to read another Article

